What is Cloud Governance?
Cloud governance is a set of rules and policies adopted by companies that run services in the cloud. The goal of cloud governance is to enhance data security, manage risk, and enable the smooth operation of cloud systems.
The cloud makes it easier than ever for teams within the organization to develop their own systems and deploy assets with a single click. While this promotes innovation and productivity, it can also cause issues like:
- Poor integration between cloud systems, even within the same organization
- Duplication of effort or data between different parts of the organization
- Lack of alignment between cloud systems and business goals
- New security issues—for example, the risk of deploying cloud systems with weak or lacking access control
Cloud governance ensures that asset deployment, system integration, data security, and other aspects of cloud computing are properly planned, considered, and managed. It is highly dynamic, because cloud systems can be created and maintained by different groups in the organization, involve third-party vendors, and can change on a daily basis.
Cloud governance initiatives ensure this complex environment meets organizational policies, security best practices and compliance obligations.
Why is Cloud Governance Important?
Here are a few ways cloud governance can benefit an organization running critical services in the cloud.
Improves Cloud Resource Management
Cloud governance can help break down cloud systems into individual accounts that represent departments, projects or cost centers within the organization. This is a best practice recommended by many cloud providers. Segregating cloud workloads into separate accounts can improve cost control, visibility, and limits the business impact of security issues.
Reduces Shadow IT
The risks and costs of cloud systems significantly increase if the organization is unaware which systems and data are deployed where. It is extremely common nowadays for employees to turn to shadow IT systems when they do not get a rapid response from traditional IT services.
Cloud governance enables employees to request cloud resources in a convenient way, yet one that applies the relevant controls and visibility for the organization. Instead of turning to shadow IT, employees can receive access to cloud systems, within the organization’s compliance and budget constraints.
Reduces Administrative Overhead
Without a cloud governance program and technology solutions to support it, organizations tend to use spreadsheets or other manual processes to track cloud accounts, costs, and compliance issues, or to control access and budgets for cloud resources. This is inefficient, error prone, and breaks down at large scale.
A complete cloud governance solution enables organizations to centrally define policies and apply them to the entire cloud infrastructure. It centralizes control over access and costs, raises alerts, and makes it easier to respond to violations. This saves time and effort, reduces the risk of non-compliant activities and unexpected cloud costs.
Improves Cloud Security Issues
A cloud governance model establishes an authentication strategy to protect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information. It allows the organization that no matter where data exists or critical systems are deployed, there will be visibility of sensitive information and assurances that the appropriate security controls are in place.
Cloud Governance Model Principles
The following five principles are a good starting point for building your cloud governance model:
- Compliance with policies and standards—cloud usage standards must be consistent with regulations and compliance standards used by your organization and others in your industry.
- Alignment with business objectives—cloud strategy should be an integral part of the overall business and IT strategy. All cloud systems and policies should demonstrably support business goals.
- Collaboration—there should be clear agreements between owners and users of cloud infrastructure, and other stakeholders in the relevant organizational units, to ensure they make appropriate and mutually beneficial use of cloud resources.
- Change management—all changes to a cloud environment must be implemented in a consistent and standardized manner, subject to the appropriate controls.
- Dynamic response—cloud governance should rely on monitoring and cloud automation to dynamically respond to events in the cloud environment.
How to Design and Implement a Cloud Governance Framework
The following are the primary components of a cloud governance framework.
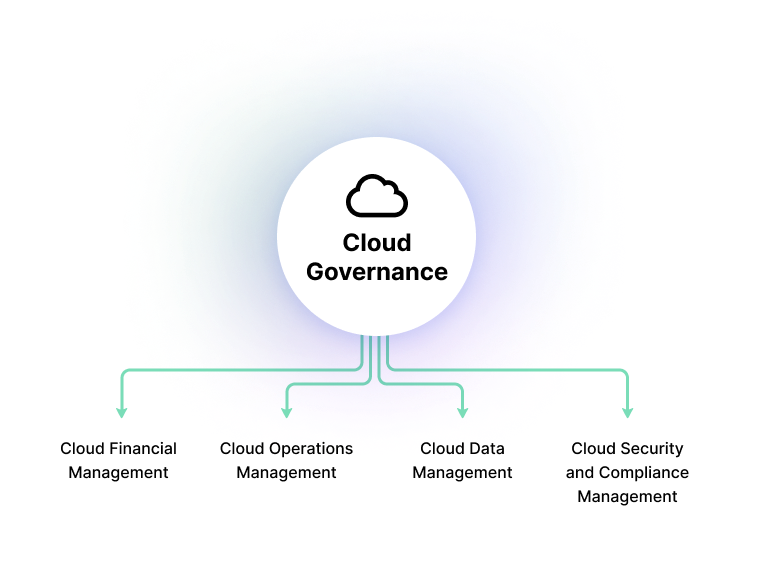
Components of a cloud governance framework
Cloud Financial Management
In many organizations, cloud costs quickly get out of hand. Cloud services often promise to reduce IT costs, but this only holds true if costs are duly managed. There are three elements of cloud financial management:
- Financial policies clarifying how the organization plans to use the cloud. For example, policies can define in which cases managed services should be used to reduce in-house operating costs, or specify a cost management checklist that must be followed before deploying new cloud services.
- Budgets define the specific allowance for different parts of the organization or different categories of cloud services.
- Cost reporting is difficult to achieve in a consistent way. Some cloud services have unpredictable charges that can appear in different places of the cloud infrastructure—for example, cloud snapshots used for backup can be stored across different regions and accounts. You can use cost reporting tools provided by the cloud vendor, or adopt third party tools that cover multiple clouds.
Cloud Operations Management
Operations management involves defining processes for deployment of services. These processes should include:
- A clear definition of resources allocated to the service over time
- Service-level agreements (SLAs) to define expected performance
- Ongoing monitoring to make sure SLAs are met
- Process and required checks before deploying code to production
- Access control requirements
Strong cloud operations management is an excellent way to prevent shadow IT. It can conserve costs by preventing unnecessary use of cloud resources, and can dramatically improve the return on investment of cloud expenditure in the long term.
Cloud Data Management
The cloud makes it easier to collect and analyze huge amounts of data, but this makes data management a much bigger challenge. Cloud governance should specify how to manage the entire data lifecycle in the cloud. This includes:
- Building a data classification scheme, and setting policies for data at different levels of sensitivity
- Ensuring all data is encrypted, at rest and in transit
- Putting in place appropriate access controls for each type of data
- Using data masking to reduce the risk of sensitive data when it is used for scenarios like development, testing, or training
- Developing a tiering strategy, moving data over time from high cost fast access systems to lower cost archival systems
- Ensuring that data lifecycle management is automated—this is critical to apply policies in large scale cloud deployments
Cloud Security and Compliance Management
Cloud governance takes responsibility for all the key topics of enterprise security. It determines what are the organization’s security and compliance requirements, and ensuring they are enforced in the cloud environment:
- Risk assessment
- Identity and access management
- Data management and encryption
- Application security
- Disaster recovery
Cloud governance should strike a balance between business drivers and requirements, real security risks, and the requirements of compliance standards. It should use existing policies and security practices, extending them to the cloud and translating them to the cloud environment.
Cloud Governance with Imperva
Imperva supports cloud governance initiatives with solutions that provide data discovery, classification and masking.
Beyond cloud governance, Imperva protects all cloud-based data stores to ensure compliance and preserve the agility and cost benefits you get from your cloud investments:
Cloud Data Security – Simplify securing your cloud databases to catch up and keep up with DevOps. Imperva’s solution enables cloud-managed services users to rapidly gain visibility and control of cloud data.
Database Security – Imperva delivers analytics, protection and response across your data assets, on-premise and in the cloud – giving you the risk visibility to prevent data breaches and avoid compliance incidents. Integrate with any database to gain instant visibility, implement universal policies, and speed time to value.
Data Risk Analysis – Automate the detection of non-compliant, risky, or malicious data access behavior across all of your databases enterprise-wide to accelerate remediation.









